CLIMATE FINTECH: USING DATA AND AI TO FIGHT CLIMATE CHANGE AND CREATE BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES

HIGHLIGHTS
- Amid dire climate warnings and devastating weather events, calls for corporate sustainability and global decarbonization are ringing louder than ever.
- A host of new “climate fintech” companies solutions leverage Big Data and AI to help enterprises assess their climate risk, monitor their operations and supply chain, and report on their ESG efforts in order to meet their sustainability targets.
- As large organizations including Citi work towards a net-zero carbon future for themselves and their clients, partnering with climate fintechs could help accelerate efforts and provide a strategic advantage.
2020-2021 will be remembered not only as the time of COVID-19, but also as the time when the climate crisis became all too real. Amid myriad devastating weather events, the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report warned that climate change is widespread and intensifying: without immediate and large-scale reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, limiting warming to 1.5°C will be beyond reach.
On a positive note, 2020 was also a record year in the amount of capital committed to decarbonization and the regulatory push for environmental disclosure and transparency. We are witnessing the rapid rise of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) activism from investors, driven by a new generation of consumers who prioritize these issues.
Companies that continue with business as usual thus face a variety of emerging risks: physical risk, supply chain risk, and reputational risk. As a result, ESG is now being embedded in business strategies and used as a foundation for building operational resilience, sustainable profitability, and a strong reputation. Citi, for example, has committed to facilitating $1 trillion in sustainable finance by 2030 and reaching net-zero emissions by 2050.
However, financial institutions (FIs) face key challenges on the path to net-zero—particularly around poor or unavailable data and little standardization in climate-related reporting. To support FIs in overcoming these challenges, a new landscape of “climate fintech” startups has emerged. These companies leverage Big Data, AI, and blockchain technology to help accelerate the “greening” of capital flows and make every FI and citizen a climate-conscious asset owner. By using alternative data sources and forecasting tools to provide actionable ESG and climate insights, climate fintechs are driving exciting new value propositions for people and corporations alike.
Climate Fintech Landscape and Areas of Opportunity
Climate risk assessment platforms offer data and tools that businesses can use to analyze the potential financial impact and disruption of different climate change scenarios. Startups in this space leverage alternative data sources (e.g., satellite, air, land, and ocean-borne sensors) and advanced climate modeling to tackle two main types of risk:
- Physical risks resulting from climate change, such as property damage or loss of business. These can be driven either by climate events (e.g., hurricanes and wildfires) or long-term shifts in climate patterns (e.g., higher temperatures)..
- Transition risks related to technology, policy, legal, and market changes enacted to adapt to climate change and transition to a lower-carbon economy
Physical risk prevention protects assets, while awareness of transition risk ensures that companies are prepared and remain relevant as their environment evolves.
In recent years, several startups have cropped up to help assess and address this risk. The Climate Service, for example, uses extensive data sources and 80-year forecasting models to analyze the impact of physical risks on assets. Other platforms, including Arcturus, use deep learning models and insights about corporate innovation and behavioral change to generate predictive assessments of corporate energy transition risk, climate pathways, and portfolio-level environmental exposures.
Corporate ESG Assessment and Reporting
New corporate ESG assessment providers offer software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms that complement self-reporting with direct feeds, APIs, and third-party corporate, financial, and specialized datasets. Sustainability measurement and reporting tools such as Diginex use blockchain to help streamline data collection, whereas Watershed helps corporates analyze and report on their emissions while providing guidance on how to reduce and offset them.
In addition to assessing direct and energy consumption-related carbon emissions (known as “Scope 1” and “Scope 2” emissions), startups are developing tools to capture and measure indirect emissions that occur in upstream and downstream value chains. These “Scope 3” emissions are the next frontier of impact quantification and management.
ESG Intelligence and Data Analysis
ESG intelligence providers such as Kayrros and Orbital Insights analyze geospatial data (e.g., satellite imagery) and environmental indicators (e.g., energy consumption, deforestation, and air quality) for insights into resource use and industrial activity.
Other providers such as IntegrityNext offer real-time monitoring of potential ESG issues in supply chains, including labor practices, safety incidents, complaints, and adverse media mentions. Still others, such as Sylvera, provide solutions focused on accessing, selecting, and monitoring decarbonization assets to better enable carbon-offsetting investments.
Consumer-Focused Solutions
Several ethical and sustainable investing platforms—e.g., OpenInvest—and a new wave of “green neobanks” such as Tomorrow are enabling their customers (many of whom are in younger generations) to spend, save, and invest their money sustainably. Meanwhile, Doconomy is offering a credit card with a carbon cap on spending, with a goal of reducing its users’ carbon footprint by half before 2030.
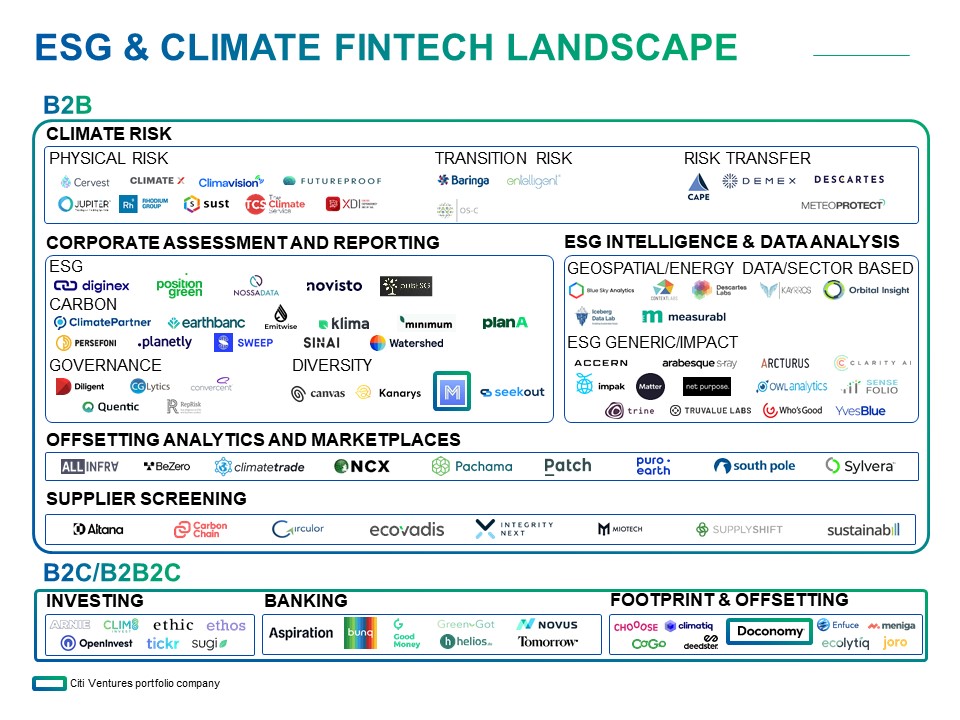
Source: Citi Ventures
Partnering with Climate Fintechs to Mitigate ESG-Related Risks and Capture Opportunities
Executing on the plan to transition to a net-zero economy will be hard work and will require a coordinated effort amongst our full set of stakeholders.
Using ESG and climate data and tools provided by startups such as The Climate Service and Watershed can help banks meet regulatory requirements, reduce their environmental footprint, and enable their clients’ net-zero strategies. Including sustainability and climate metrics in supplier selection and financing can support supply chain resilience and contingency planning, while embedding ESG indicators into asset selection, credit, and market risk metrics can help future-proof portfolios. Finally, including ESG data in product design and marketing can help banks capture opportunities from the rising demand for sustainable products among retail customers.
For large organizations, strengthening relationships with ESG data and analytics startups and embedding their solutions in key business processes will be the winning strategy that can drive long-term, sustainable growth. We expect that more companies will explore commercial partnerships with ESG solution providers. Truvalue Labs, for example is collaborating with banks to gain a deeper understanding of the ESG opportunities and risk landscapes for their clients—and that more opportunities will arise to pursue capital investments in this vital emerging space.
For more information email Jelena Zec at jelena.zec@citi.com or Alix Brunet at alix.brunet@citi.com.
For more on ESG and innovation, click here.

